- The riverbed where water remains pernamently
;
- The mid riverbed, river basin which is
ordinarily occupied by the riparian forest (dense and varied
végetation borderng the river), which flows over
periods of 1 to 10 years on average. The mid riverbed is
subjected to frequent risk of flooding, the water velocity
and transport of sediment during floods are important ;
- The floodplain is occupied by a river
during floods. Outside the floodplain,river flood risk is
zero ( which does not exclude the risk of flooding by stormwater
runoff, especially in urban areas.
THE
TYPES OF FLOODS
There are three main types
of floods :
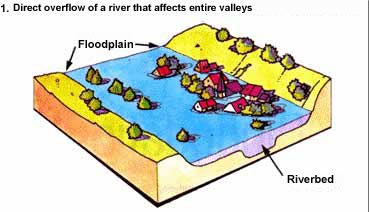
Direct
overflow : A flood can occur when a
river
overflows and stream out of his riverbed to occupy
her major bed then he invades entire valleys.
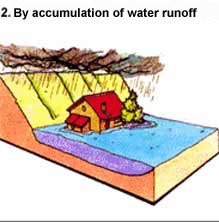
By
accumulation of water runoff : when there is insufficient
capacity
of infiltration, evacuation of soils or drainage system during
the abnormal
rainfall. These floods can occur in built-up areas, outside
the bed of the watercourse
itself, when impede the normal flow of intense rainfall, soil
sealing and design
of urbanization and of networks sanitation (thunderstorms,
especially of cevenol type).
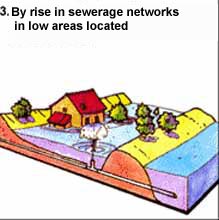
Indirect
overflow : water date back to through
the alluvial groundwater in sewer systems
at low points located... by siphoning
But a flood can result in other more or less
current phenomena :
-during a
storm, a hurricane or
a tsunami there is often a flooding of coastal zones
;
- during the destruction of
a work (dams) ;
- during sudden floods ;
Left,
in Saskatchewan, dry creek Indianhead the07/17/1996.
Right, same creek in flood the 04/10/1996.
.gif)
THE
CAUSES
MANY
FACTORS INVOLVED IN EUROPE :
- Often the three areas of watercourses (minor
riverbed, mid riverbed and floodplain) are transformed by
human activity or climate change. So with a more favorable
soil to runoff there is a decrease in the permeability of
the entire basin due to deforestation, forest fires, the multiplications
of coated surfaces (roads, houses, ...) and then makes more
brutal floods.
- The distribution
and intensity of rainfall in the watershed (which is the
place where the rivers collect water from a territory more
or less large) and duration of precipitations.
- In Europe
at the end of the spring and early summer during warm spell,
heat waves
or situation of the foehn
wind that causes a significant melting of snow.
- In spring, the ice break-up
of the rivers in the mountains (Alps, Pyrenees), or in countries
at high latitudes as Canada which are dams when it freezes
in winter can also cause flooding.
- Severe
thunderstorms in summer and spring which cause violent
rainfalls.
- In autumn
stormy rainfall, especially on the Mediterranean coast have
effects that can be felt throughout the southern half of
the country France.
- In northern
and western France oceanic rains cause flooding, especially
in winter and spring.
- The importance of absorption
by the grounds and infiltration in the basement which feeds
the groundwater affects flooding. Saturated soil by recent
precipitations doesn't absorb, which could cause flooding
with more precipitations.
THE
MAIN CAUSES FLOOD IN OTHER COUNTRIES ARE :
- Monsoons in
India, Bangladesh and other countries resulting in heavy rainfall.
- Storms or cyclones followed by heavy rains
cause flashfloods, landslides, mudflows and flooding. This
is often followed by a phenomenon called "storm
tide".
- During El
Niño or La Niña there
is an increase in precipitation in some countries around the
Pacific causing floods see stronger monsoons.

Flooding in Texas 07/06/2002
|
|

Flooding in India
during the monsoon
|
.gif)
WARNING
Patricia
Régnier helped me correct mistakes, please you to visit
her
blog
I’m not english speaker, some improprieties can appear
to english masters.
Could you help me reporting by mail any fault you read. Thank
you for all.
Contact :






