1st PART
In climatology,
a drought is a long period of time during which no rain falls
we speak of drought when precipitations
are unusually low compared to normal. In France and in neighboring
countries, it is called "absolute drought" a period
of at least 15 consecutive days without a drop of water (or
less than 0,20 mm per day).In the United States, it is said
that there is drought when a large area receives only 30%
or less precipitation than normal in twenty-one days minimum.
In Australia, there must be a region receives less than 10%
of rainfall compared to the annual average and India requires
that annual precipitation are 75% lower seasonal norms to
talk about drought. Often in summer waves of heat occur. These are periods (ranging from one day to several months) of extreme heat.
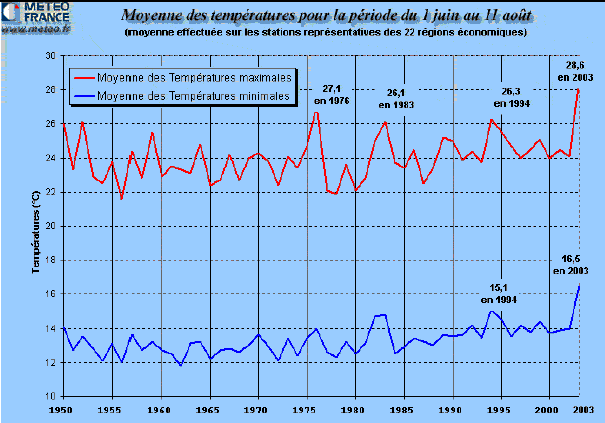
The minimum and
maximum temperatures average of the TYPES OF DROUGHTS There are 3 types of droughts : - Atmospheric drought is related to lack of precipitation. It is judged by the amount of water collected in the rain gauges ; - Agricultural drought is based on moisture content of agricultural soil to 1 meter deep. When it occurs, the soil water reserve of plants runs out and can have dramatic effects on plants. This slows the rise of sap ; - hydrological drought is the decrease of streams and rivers. It comes after the depletion of water reserves in the soil. At this level, we speak about hydrological drought. When the situation gets worse, then the water tables and the groundwater progressively disappear. CAUSES OF DROUGHTS AND HEAT WAVES Summer droughts and heat waves occur when a large anticyclone stays long standing above the country and keeps away the Atlantic depressions that bypass it.
08/05/2003
an anticyclone was above Europe so an air mass of Africa is
In many countries droughts are related to anomalies of the surface temperatures of the Pacific water. While El Niño can affect droughts. When this climatic phenomenon occurs the Indonesia, Australia, Japan, South Africa, Chile, Brazil and Alaska are affected by droughts and severe heat waves. It said there would be a dry or and hot weather with a cycle of 28 years in Western Europe. In 1921 a very important drought occured in Europe and in 1949 a hot, dry summer and the summer 1976 was also very hot and dry and is 28 years after a major drought returned in 2003. What is the cause of this cycle that it is not yet known. WHERE OCCUR MOST OFTEN THE DROUGHTS ? Droughts can occur almost everywhere in the world. Except in the polar and subpolar regions the only areas that don't go through drought.
A video on the causes and consequences of the drought.
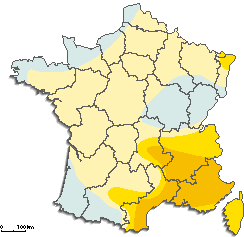
This map shows us that drylands are everywhere, but especially in the tropics of cancer and Capricorn.
Droughts in France:
the annual number average of sequences of more than
THE IMPACT OF DROUGHT As the drought continues, it causes a lot of negative effects : - The level of the water table down ; - The level of lakes and rivers runs out disrupting river traffic ; - Water restrictions may affect crop irrigation, domestic water uses such as watering gardens or industrial samples ; - A reduction or even loss of crops ;
In July 2003 a severe
drought has affected several European countries Comparison between
the Elbe with a high level during the rainy year WARNING
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||