1st PART
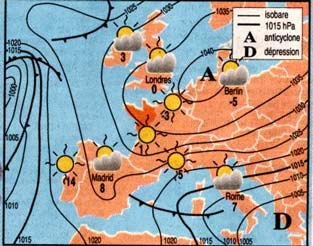
CAUSES SEVERE AND MILD WINTERS SEVERE WINTERS In winter, in the mid-latitude climate dynamics is often characterized by strong winds from the west which repel cold air from Asia and we bring the heat stored during the summer in the surface layer of ocean. But the cold air can be more or less led to France : The Baltic Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea have influences on air flow, especially when their speeds are low. When the cold air comes from the north ... the Alps are a barrier to the wind and protect Italy. Depending on the height and thickness of the mountainous terrain, these are roadblocks to progression and direction of cold. But according to the position and importance of anticyclones the cold air can be directed to France and Britain in three different ways : - Let the air comes from Arctic when the anticyclone coming from Greenland to reach Britain and France.
- Either the air is continental origin when surface zones of high pressure from Siberia pushes the cold air to Western Europe.
- Let this air is supplied by an anticyclone located on the Nordic countries and a stream of North East which grows cold in the direction of Britain and France. This situation is relatively happened even if it is what is passed in February 1986.
MILD HIVERS As for the cause of cold winters the position and strength of anticyclones are also the source of mild winters. When the anticyclone is located south of France warm air from North Africa sometimes rises to Britain.
RESUME
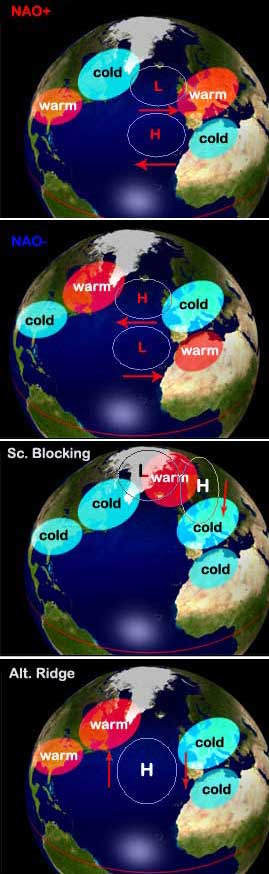
When in the North Atlantic, atmospheric circulation is cut off by blocking anticyclones, the flow passes to the north or north east to Europe but in the west of the USA the flux passes to the south. These blocking situations vary according winters, especially according to the phenomenon NAO (North Atlantic Oscillation), that is the oscillation of the differential pressure between Iceland and the Azores. It was also shown that for three-quarters of the time the cold periods that Europe suffers in winter the NAO index is often negative, whereas if the index is positive the winters tend to be mild in western Europe. Cold waves seem to occur especially during the period of low level of 11 years cycle of solar activity and the reverse during the period of significant solar activity, even if this solar cycle has little influence on the climate compared to some climatic phenomena. But other solar cycle have more effect than this latter. From 1645 to 1715 there was a minimum long-term and important called the "Maunder Minimum" solar activity. This takes place in a period when there were many harsh winters and they were much colder than today.
THE PERCENTAGE OF COLD WINTER SEE ROUGH
OR MILD OR
Each winter is not the same severity and duration. Through individual and science journals, this memory tells us about the climate of the past. - In 11th century, in France the winter 1076/1077 was the toughest among the three strong winters known from testimonies of contemporaries. - In 12th century, there were at least four very cold winters and two very mild winters in Europe. - In 13th century, the winter 1242/1243 was particularly severe in Britain. - In 14th century, there were nine very cold winters in west Europe. - In 15th century, the winter 1407/1408 was the most severe of the 15 strong winters in the Middle Ages in France. - In 16th century,there were 23 winters harsh. - In 17th century, among the 24 winters that of 1659/1660 was perhaps the coldest in Europe. It was the coldest period in Asia. - In 18th century, 16 winters were very cold with that of 1708/1709 was so cold that we had never seen in France according testimony. - In 19th century, the winter 1879/1880 was one of the coldest of the century with 75 days of frost respectively among 25 very cold winters in France. This century has been the coldest for North America. - In 20th centuryle, about the 23 very cold winters that of 1962/1963 and 1955/1956 were harsh in Europe. - In
21th
century, winter 2005/2006
is currently the coldest winter in Europe with an anomaly
of the average temperature of -1,50°C for France and with
the lowest number of days of sweetness. This is the tenth
coldest winter recorded since 1950. But the 2009/2010 winter
was very cold in France, Finland, Great Britain ... and mostly
snowy. In Britain it is the coldest winter since 1978/79 with
a temperature anomaly of 28,22°F (-2,10°C). WARNING |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



.jpg)