|
1st
PART
On our planet, the majority of the heat is stored in the oceans. They retain more easily the energy than continents and more than the atmosphere. So the ocean plays a role as important as atmosphere on the climate.
Under normal conditions the thermocline
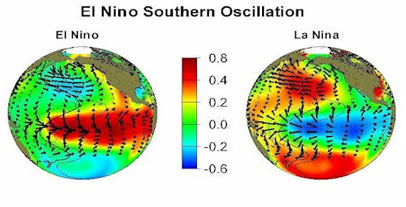
is not flat. Its depth is about In the tropical Pacific, the irregular changes of sea surface temperature (S.S.T. : sea surface temperature) which occur, ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation) cause local disturbances and have climatic effects. The two opposite phases of this phenomenon are : El Niño and La Niña. When there is no significant SST anomalies then it is named La NADA..
The sea surface temperature anomalies
during Evolution from La Niña to La
Nada and to El Niño These climate changes are the most important after the season and particularly affecting Africa, Australia, South Asia and America. Click
here to see this larger schema which Scientists use the data from the TAO (Tropical Atmosphere Ocean) / TRITON studying climatic variations from year to year related to El Niño / La Niña and consists of 70 moored buoys spanning the equatorial Pacific between 8° North and 8° South. They measure the atmospheric conditions of the surface (wind, humidity, precipitation, radiative flux) and ocean surface conditions and subsurface down until to 500 m of depth (temperature, currents and salinity). All is organized by the United States, France, Japan, and Taiwan. Their data confirmed the relationship between changes in the volume of hotter water than 20°C from 0 to 300 m of depth (WWV) and the phenomenon of the cycle of El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Because it was also found that the magnitude of the SST anomalies of ENSO is directly related to the magnitude of the anomalies of the WWV zonal averages.
If the WWV is compared to the anomaly of the equatorial
Pacific SST, it is easy to see
It was in 1920 that a British mathematician Gilbert Walker discovered that when the barometric pressure is higher than normal in the South Pacific, it tends to be lower than normal in the Indian Ocean, and the usual winds are appearing with abundant rain. This climatic phenomenon occurs every 2 to 7 years.
During the El Niño phenomenon
the thermocline descends in Eastern
This phenomenon is relaed to the instability of the couple atmosphere-ocean. Two types of waves travel in the Pacific. Kelvin waves propagate eastward and Rossby waves westward. The slow movement of the ripples and the variation of atmospheric pressure could be one of the causes of El Niño and la Niña. The lower the pressure near Indonesia and Australia, and the higher the pressure near Easter Island, then trade winds are stronger sweeping the tropical Pacific from the eastern Pacific ocean to the west. Warm sea surface water accumulated in the western Pacific by these winds push up the sea level of about 50 cm higher and thermocline level is lower near Indonesia than Ecuador. But when the pressure increases much near Indonesia and Australia and then decreases near Easter Island (Chile), there is an anomaly of the west wind in the central Pacific and the trade winds weaken. Then the warm surface waters are driven towards the East. The surface layer becomes thinner upstream and downstream plunges. To the east, this increases in depth is balanced by Kelvin waves that propagate rapidly (3 m/s). After three months, when they arrive near the western coast, the waves prevent the upwelling of cold waters rich in fishes. The increasing in depth of the thermocline in the east directly affects sea surface temperature increasing. Then the air is warmed by the increase in the temperature of the ocean. In the Western Pacific ocean, the upwelling of the thermocline is spread in the form of Rossby waves.
Description of ENSO (El Niño and la Niña)
The westerlies and trade
winds converge on the area of warm waters
WARNING
|



 NORMAL EL NINO CLASSIC LA NINA CLASSIC
NORMAL EL NINO CLASSIC LA NINA CLASSIC 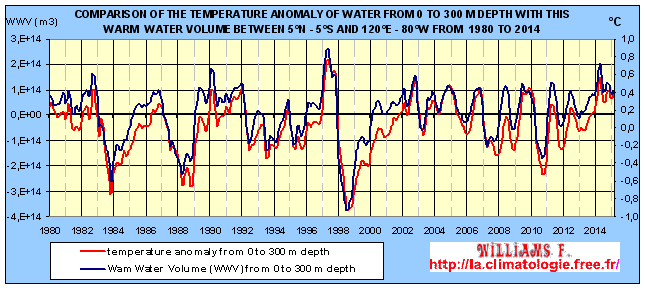

.gif)
