 . .
|
6stPART
 |
|
|
|
THE SANTORINI
:
About 1645 ± 20 BCE in the Mediterranean between Greece and Turkey one super volcano the Santorini also named Thera exploded. It would have ejected three times more aerosols in the atmosphere than the Krakatao up to 35 km altitude. The explosion was heard at least over 6000 km and climate was disrupted for ten years in the Middle East. It was 10 times larger than the Mount St. Helens volcano.
This eruption would have created a large tsunami in the Mediterranean with a wave of 60 meters high during the collapse of the caldera of the volcano which is partially embedded, according to researchers, because stones composed of a floating material were found all around at height 60 meters.
The consequences of this eruption on climate, and the tsunami ... could even explain some astonishing phenomena recounted in the Bible and the 10 plagues of Egypt. In this country of intense rains occurred because of aerosols while it is rare in this country. Then there were hailstorms, possibly caused by the ice accretion around the particles of the volcano. The sky would have been veiled by the ejected gas and ashes.
The last major eruptions are those of 726, 1650, 1926.
|
|
|
KIKAI
:
There were about 6.300.years the Kikai had a strong eruption, one of the largest eruptions on Earth of the past 10.000
years. . About 150 km3
of ash were ejected. The volcanic explosion index of the eruption was 7. There were pyroclastic flows 100.km across the sea to southern Kyushu and ashes fell across Japan.
volcano is a caldera submersible with three small islands. Its diameter is about 19.km diameter. Submersible topography suggests the presence of a double structure collapse. This volcano has had three major eruptions.
The last major eruptions are those of 500 (VEI 3), -1090 ± 100 (VEI 2) and -6.300.ans (VEI.7).
|
|
THE TOBA :
There are 75 000 years there has been the most important eruption of recent million years. It was the eruption of Toba in Sumatra, Indonesia. This volcano would expelled 800 km3 of ashes and 1000 km3 of lava over a thickness of about 50 m to the coasts of the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea. The energy released was equivalent to 40 millions atomic bombs Hiroshima type . Most of India was under the volcano ashes after eruption. The Earth could have experienced a decline in temperatures estimated around 62,6°F (17°C), in the middle and high latitudes approximately but this impact is hard to detect because of the concurrent glacial conditions. This is what is called the "volcanic winter" and lasted 6 years according analysis. The ashes was spread over 2,5 millions
kilometers. And in South India an ash layer of 15 cm fell.
|
 A caldera long of 100 km and 30 km
A caldera long of 100 km and 30 km
deep was created during its eruption
so the largest of volcanoes |
|
LONG
VALLEY :
The Long Valley is located at east of California at 3390 m altitude.
During the eruption there are 730 000 years, 600
km3 of tephra and 580 km3 of lava have been ejected.
After this eruption the top of the magma chamber was collapsed creating the caldera of Long Valley of elliptical form (15km to 30km).
Other important eruptions occurred there are: 500.000, 300.000, and 100.000 years.
|
|
|
THE YELLOWSTONE
:
The supervolcano is located to the west of the USA in Yellowstone National Park on almost
898.300 d'hectares (88.x.95.km).The caldera of supervolcano that spans a huge area of 75.x.45.km
from Northeast to southwest across the Yellowstone is 8 km deep.
There are 2 millions, 1,60 millions and 640.000
years to near 100.000 years, it had an eruption among the most violent of the last millions years. Its eruption could be 1000 times more violent than that of Mount St. Helens is 50 times more than the most violent bomb. This volcano could be the cause of the glaciations Biber or Donau or the Gunz that took place during its eruptions. It explodes on average every 600.000 years.
This volcano has ejected 280 Km³, 1000 Km³ and
2500 Km³ of ashes on earth. Half of the USA have been covered by the ashes of which a layer of 1 m in Denvers at the last eruption.
If this volcano exploded lava would ejecte up to 24 km high ! The temperature would drop to 53,6°F (12°C) and snow would fall at the equator. It would plunge the world into a terrible glaciation.
The next eruption is expected in the next 100.000 years like the past three eruptions have had regular intervals of 600.000
ans. 50% of molten rock must be in the magma chamber before the eruption and there should be only 10%. But the volcano evolves and the ground has 1.m
rise by around in 75 years if the current rate of expansion continues ! This is due to the magma chamber.
|

Yellowstone Park seen from space. The dark caldera, which occupies the center of the image is the crater of the volcano.

To get an idea, here's what would an explosion of this super-volcano
|
THE VOLCANOES THAT HAVE OR MIGHT HAVE
HAD THE MOST INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE
|
DATE OF THE ERUPTION
|
NAME OF THE VOLCANO
|
VEI
|
COUNTRY
|
AMOUNT OF DUST EJECTED
INTO THE ATMOSPHERE
|
LOWERING THE TEMPERATURE ON THE GROUND CAUSED BY THE VOLCANO
|
|
from 15 to
08/21/1991
|
The Hudson
|
+5
|
Chile
|
30 cm of ash on the ground but not high in the atmosphere
|
..
|
|
06/15/1991
|
Pinatubo
|
6
|
Philippine
|
20 millions tonnes of sulphur is 25-35 km3 of stratospheric aerosols
|
decrease in global temperature of 32,9°F (0,50°C) from 2 to 4 years after the eruption.
|
|
11/13/1985
|
The Nevado
del Ruiz
|
3
|
Colombia
|
0,56 km3
of stratospheric aerosols
|
.
|
|
03/25/1982
|
El Chichòn
|
5
|
Mexico
|
12 km3
of stratospheric aerosols is
20 millions tonnes of sulfur
|
in the northern hemisphere a lower 32,54°F (0,30°C) two months after the eruption.
|
|
05/18/1980
|
The Mt
Saint-Helens
|
5
|
USA
|
540 000 tonnes is 0,55km3 d'aérosols stratosphérique
|
32,18°F (0,10°C)
|
|
01/22/1976
|
St. Augustine
|
4
|
Alaska
|
0,60 km3
of stratospheric aerosols
|
.-
|
|
10/10/1974
|
The Fuego
|
4
|
Guatemala
|
3-6
km3 of stratospheric aerosols
|
-.
|
|
03/17/1963
|
Agung
|
5
|
Island Bali in Indonesia
|
10-20 millions tonnes is 16-30 km3 of stratospheric aerosols
|
32,54°F (0,30°C)
for 3 years
|
|
06/06/1912
|
Katmai
|
6
|
Alaska
|
20 millions of sulfur is 35 km3 of ash emission
|
32,36°F (0,20°C)
|
|
1902
|
Santa Maria
|
4
|
Guatemala
|
20 millions tonnes of sulfur
|
32,72°F (0,40°C)
|
|
06/10/1886
|
Tarawera
|
5
|
New Zealand
|
0,30 Km³
of ash would have been ejected. The eruption cloud reached an altitude of 10 km
|
.
|
|
09/06/1883
|
St Augustine
|
4
|
Alaska
|
5,10±0,04X108
m3 of tephra were ejected
|
-
|
|
08/26/1883
|
Krakatoa
|
6
|
Indonesia
|
50 millions tonnes of stratospheric aerosols in the northern hemisphere and 30 to
38 millions tonnes in southern hemisphere.
|
32,54°F (0,30°C)
|
|
04/10/1815
|
Tambora
|
7
|
Indonesia
|
200 millions tonnes of sulphur is 7 times more than Mount St. HelenF
|
32,72 to 33,26°F (0,40 to 0,70°C)
|
|
1814
|
Mayon
|
4
|
Philippines
|
550.000
km3
of tephra
|
.
|
|
1813
|
Vesuve
|
3
|
Italy
|
75.000
km3
of tephra
|
.
|
|
1812
|
The Awu
|
4
|
Indonesia
|
550.000
km3
of tephra
|
.
|
|
04/27/1812
|
Soufriere
|
4
|
Guadeloupe
|
550.000
km3
of tephra
|
..
|
|
06/08/1784
|
Laki or Lakagigar
|
4
|
Iceland
|
from 80 to 100
millions tonnes of sulfur
|
33,80°F (1,00°C)
|
|
05/09 to 08/05/1783
|
The Asama
|
4
|
Japan
|
0,45 to 0,50
km3 is 200 times less than that attributed to the eruption of the Tambora
|
around 33,80°F (1,00°C)
|
|
06/03/1660
|
Long Island
|
6
|
New Guinea
|
--
|
32,54°F (0,30°C)
|
|
1641
|
Parker
|
5?
|
Phillipine
|
--
|
32,90°F (0,50°C)
|
|
02/19/1600
|
Huaynaputina
or
Huayna-Putina
|
6
|
Peru
|
100 millions
tonnes of sulfur
|
33,44°F (0,80°C)
|
|
1580
|
Billy Mitchel
|
6
|
Islands Salomont
|
.
|
.
|
|
1452
|
Kuwae
|
6
|
New Caledonia in Vanuatu
|
It would have ejected the same amount of dust as the Santorini and Mazama
|
32,90°F (0,50°C)
|
|
1150
|
Quilotoa
|
6
|
Ecuador
|
.
|
.
|
|
1050
|
Baitoushan or Changbaishan
|
+6
|
East of China
|
96
km3 Tephra.
|
.
|
|
934
|
Eldgja
|
4
|
Iceland
|
9
km3 of lava and tephra
|
-.
|
|
930
|
Ceboruco
|
6
|
Mexico
|
.
|
.
|
|
02/20/535
|
Krakatoa
|
6
|
Indonesia
|
.
|
.
|
|
450
|
Ilopango
|
6
|
Savadore
|
.
|
.
|
|
416
|
Krakatoa
|
.
|
Indonesia
|
.
|
.
|
|
240
|
Ksudach
|
6
|
At the Kamchatka peninsula in Russia
|
.
|
.
|
|
01/15/186
|
Taupo
|
+7
|
New Zealand
|
more than 90 km3
of material and
30 km3 of ash.
|
.
|
|
08/24/79
|
Vesuve
|
5
|
Italy
|
As far as the Mount St. Helens
|
-.
|
|
60
|
Churchill
|
6
|
East of the Aleaska
|
.
|
.
|
|
50
|
Ambrym
|
+6
|
New Caledonia in Vanuatu
|
19-25 km3
of material
|
-.
|
|
-250
|
Raoul
|
6
|
Iceland
|
.
|
.
|
|
-450
|
Okmok
|
6
|
Alaska
|
.
|
.
|
|
-1050
|
Pinatubo
|
6
|
Philippine
|
.
|
.
|
|
-1350
|
Pago
|
6
|
New Caledonia
|
.
|
.
|
|
-1645 ± 20
|
Santorin
or
The Thera
|
6
|
Greece
|
3 times more than the Kracatoa. 30 km3
of ash and a cloud up to 36 km altitude
|
.-
|
|
-1860
|
Mt
Saint-Helens
|
6
|
USA
|
.
|
.
|
|
-3550
|
Pinatubo
|
6
|
Philippine
|
.
|
.
|
|
-6300
|
Kikai
|
7
|
Japan
|
expelled 150 km3
of ash
|
. |
|
-75 000
|
Lake Toba
|
8
|
Sumatra, Indonesia
|
expelled 800 km3
of ash and
1000km3 lava.
|
62,60°F (17°C)
|
|
-750.000
|
The Long Valley
|
+6
|
California
|
600 km3
of tephra ejected
|
.
|
|
-600.000
and
-1,60 millions
and
-2 millions
|
Yellowstone
|
8
|
USA
|
expelled 1000
km3
of dust it is 600.000 years.
|
53,60°F (12°C)
|
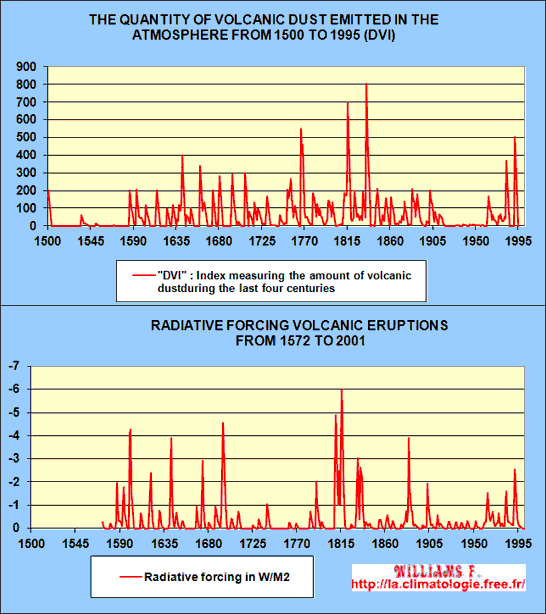
Source DVI (Index measuring atmospheric dust burden volcanic (Dust Veil Index))
of the NOAA
and source of the radiative forcing of the CRU-UEA
Click here to see a graphic showing us the total sulfate
ejected by volcanoes during these 110 345 years
.gif)
WARNING
Patricia
Régnier helped me correct mistakes, please you to visit her
blog
I’m not english speaker, some improprieties can appear
to english masters.
Could you help me reporting by mail any fault you read. Thank
you for all.
Contact :
|
|