 . .
|
5st PART
 |
|
|
|
THE
KRAKATOA :
On 08/26/1883 the krakatoa exploded (VEI 6) with a power equivalent to 10.000 times the Hiroshima bomb. An ash cloud rose to an altitude of about 27.km. The explosion was heard up 5.000.km either from India to center of Australia, in the south west of Indian Ocean Rodriguez Island was the most distant place where the explosion has been heard. Everything was covered within 160.km plunging the entire region into total darkness in broad daylight during the 22 hours of eruption. In Europe there has been a decline of 10-20% of atmospheric transparency for 3 years. This decrease in brightness due to aerosols has reduced the global average temperature of about 0,30°C. Because of the ash in the atmosphere, for 3 years at the sunset the sky turned red both in the US and in Europe... Many tsunamis occurred including one that created a wave of more than 40.m high by places !
The 02/20/535 this volcano would had an eruption of the power of two billion bombs of Hiroshima (VEI 6) ! This could be the cause of climate change at this period according the analysis of the study of tree rings, ice cores, Roman writings... Because the eruption has masked much of the light and heat of the sun for about 18 months, significantly cooling the global climate.
In 416 it is possible that the krakatoa would have exploded and created a caldera of width 7.km according the ancient book "Pustaka Raja" Javanese.
|

Eruption from 08/26/1883
Click on the photo to see a video eruption of Krakatoa in 1883 after the doc-movie : The last days of Krakatao
Click here to a video
|
|
THE TAMBORA
:
The 04/11/1815, on the island of Sumbawa Indonesian volcano Tambora awoke. The sound of explosions was heard up to 1750 km away or to Australia. A volume of 150 to 175 km3 of pyroclastics (dust and ashes) is emitted during 2 to 3 days up to 600 km away from the volcano, and were screened in the stratosphere (20 - 30 km in height) where they are then transported by the jet-streams of the upper atmosphere. For several days the sky darkens over an area equivalent of Sicily. Within months dust and aerosols spread into the atmosphere causing climate change during several years. During these periods prolonged brightly colored sunsets are reported - orange or red on the horizon.
The eruption of Tambora occured after several other significant eruptions in the Azores in 1811, in the Soufrière of St. Vincent (West Indies) and the Awu (Indonesia) in 1812, the Vesuvius in 1813 and at Mayon (Philippines ) in 1814. This explains why in 1816 Europe had a year without a summer "The year without a summer." Indeed, this summer was cold and rainy in the US and Europe, it fell 15 cm of snow in June in the US and there was frost on July 9, 21 and 30 August what has had to disastrous consequences on crops and which is causing starvation. In France, July presented a monthly average temperature deficit of 3°C at Chalons-sur-Marne and Paris, the rainfall reached there two to three times the monthly norm calculated over long periods.
Its recent eruptions took place in 1967, (VEI 0), 1880±30 (VEI 2), august 1819 (VEI 2), 1812(VEI 7), 740±150, -3050, -3910.
|
|
|
THE LAKI :
From 6/8/1783 until February 1784 the Laki in Iceland or Lakagigar had an eruption for eight months, which was one of the biggest historical disasters occurred in this island. The eruption was of fissure type. Nearly 120 million tons of sulfur dioxide were produced during this event (4 times more than El Chichon and 80 times more than Mount St. Helens). In the United States from the East, the winter mean temperature was 4,80°C below average. The evaluation for the drop in Northern Hemisphere temperature is approximately 1°C.
In Scotland in 1783 was called "year of the ashes." Volcanic dust and gases caused a bluish haze that spread during the hot summer and autumn 1783 in most of Europe and adjacent regions of Africa and Asia. The winter 1783/1984 was very cold due to sulfur dioxide emitted into the stratosphere.
|
|
|
THE SAMALAS :
In Indonesia, in 1257 the volcano erupted with a large explosion around eight and two times larger than the eruptions of Krakatoa and Tambora ejecting 40.km3 of tephra at 43.km altitude. The explosion formed a caldera 8,5 km in length to 6 km wide. Which is one of the few caldera formed by an explosion and not of the implosion of the magma chamber underlying as is more often the case. The explosion caused a temporary global cooling and reduced the harvest.
The volcano at an altitude of 3726.m above sea level and is the second largest volcano in Indonesia. Sixteen eruptions Samalas are listed since 1847.
|
|
|
THE BAITOUSHAN
or CHANGBAISHAN :
To the east of China, in about 1050 the volcano exploded with a strenght of VEI+6. It ejected 96.km3 of tephra in the atmosphere that was able to upset the climate.
At the top of the volcano there is a caldera wide of 5.km and deep of 850.m occupied by the Lake Tianchi.
Four eruptions have been recorded since the 15th century
|
|
|
THE TAUPO
:
Le 01/15/180, in New Zealand Taupo exploded (VEI + 6). The eruption resulted in deposits of several meters high and expelled more than 90.km3
of pyroclastic materials spread over 6.000 km2. The biggest volcanic cloud would be mounted to over 50.km altitude. This volcano has the largest caldera with a perimeter of approximately 193.km covering a surface of 616.km2. Its deep is 186.m maximum. It is the largest lake in New Zealand and flows out in the Waikato River.
This super-volcano would also had eruptions in : -200(VEI 4) , -900(VEI 4), -1600(VEI 6), -2600
(VEI 4), -2900 (VEI 4), -3400 (VEI 4), -4100 (VEI 4),
-4700 (VEI 4), -9430 (VEI 4), -9450(VEI +4), -9850(VEI
5) ) and there are about 26.000.years.
|
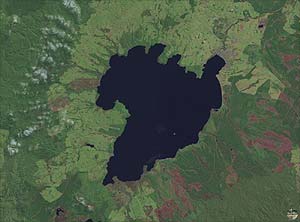
Lake Taupo in the volcano caldera seen by satellite |
|
LE VESUVIUS
:
on 08/24/79, in Italy the inhabitants of Pompeii saw one of the worst eruptions of Vesuvius. When the eruption began it got dark in the middle of the day because of all the smoke ejected in the atmosphere at height of more than 20.km as many as during the eruption of Mount Saint Helens. This would mean that the volcano has had effects on the climate too. This eruption buried the cities of : Herculaneum underneath more 16 m of a solidified mud, Pompeii under 6 m of lapilli (grains of a size between 2 and 64.mm projected with an unheard of violence by some volcanoes when they erupt) and Stabiae, located at its feet over the Gulf of Naples. The 08/25/79 the volcano cone collapsed to form a large crater over 11.km circumference.
The Vesuvius has experienced seven major eruptions is then made to forget for seven centuries. In 1766, he woke up and then there had nine eruptions in less than thirty years. The last major eruption was in 1906. The last and or major eruptions are those of there is about 3780 years (the more devastating than that of the year 79) of december 1631 (the largest after that of 79 where the layer thick ash reached 30.cm in Naples in 1632), 1766, 1832,
04/26/1872, 04/01/1906, 06/02/1929 et 03/02/1944.Since then, it dozes.
Click here to see an animation of the eruption of Vesuvius
Click
here to see a video
Opposite an animation of the height of the ash on the ground compared to the distance of the Vesuvius
|
|
SEE
MORE IN THE NEXT PAGE
.gif)
WARNING
Patricia
Régnier helped me correct mistakes, please you to visit her
blog
I’m not english speaker, some improprieties can appear
to english masters.
Could you help me reporting by mail any fault you read. Thank
you for all.
Contact :

|
|